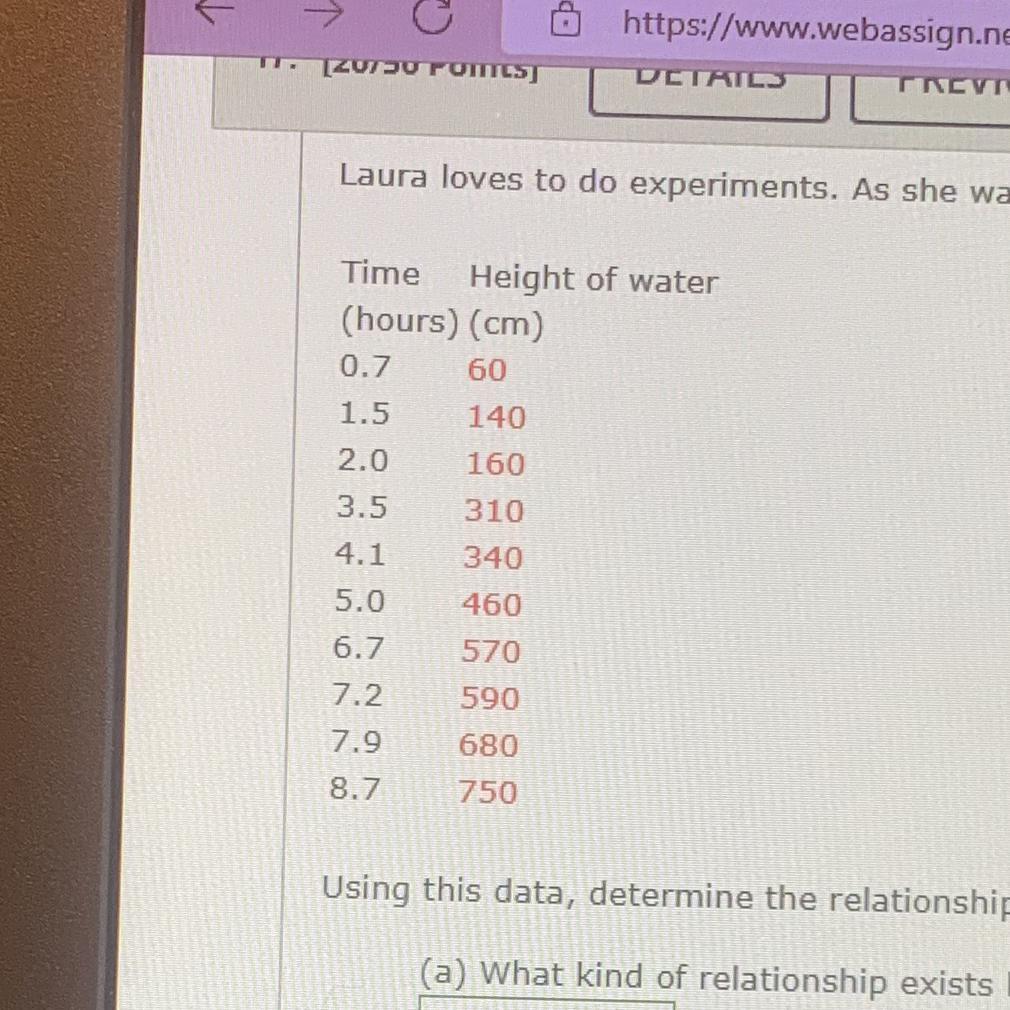
What is the height intercept?(b) What is the slope of the line?185.5 cm/hours(c) What is the height intercept?(d) Assuming Laura started with an empty pool at time = 0 hours, you would expect the height intercept to be zero. Unfortunately due to error in measurements theintercept was not zero. Use the 5% Rule to calculate the height intercept error. What is the the height intercept error?(e) What would you expect the height of the water to be after 14 hours?
Answers
C) the height intercept would be 0 given the pool has no water at the beggining.
D) To find the vertical axis intercept error, we will need to use the formula
[tex]Error=\lvert{\frac{vertical\text{ }Axis}{Largest\text{ }Value}}\rvert *100[/tex]Related Questions
A car has a velocity of 21.3 m/s. It then accelerates at a uniform rate of 3.6 m/s per second for the next 5.0 seconds. What distance does the car cover during this time? Round to 4 decimal places if necessary
Answers
Explanation
U uniformly accelerated motion is the one in which the acceleration of the particle throughout the motion is uniform,the formula to find the distance is as follows:
[tex]\begin{gathered} x=v_ot+\frac{1}{2}at^2 \\ where \\ v_o\text{ is the initial velocity} \\ t\text{ is the time} \\ a\text{ is the acceleration} \end{gathered}[/tex]so
Step 1
a)let
[tex]\begin{gathered} v_o=21.3\text{ }\frac{m}{s} \\ a=3.6\frac{m}{s^2} \\ t=5\text{ s} \end{gathered}[/tex]b) now,replace in the formula and calculate
[tex]\begin{gathered} x=v_{o}t+\frac{1}{2}at^{2} \\ x=21.3\frac{m}{s}*5s+\frac{1}{2}3.6\frac{m}{s^2}*(5\text{ s\rparen}^2 \\ x=106.5\text{ m}+45\text{ m} \\ x=151.5\text{ m} \end{gathered}[/tex]therefore, the answer is 151.5 meters
I hope this helps you
After traveling for 6.0 seconds, a runner reaches a speed of 12 m/s after startingfrom rest. What is the runner's acceleration?
Answers
Given data:
Initial speed of the runner as he starts from the rest;
[tex]u=0[/tex]Final speed of the runner;
[tex]v=12\text{ m/s}[/tex]Time taken;
[tex]t=6.0\text{ s}[/tex]The acceleration of the runner is given as,
[tex]a=\frac{v-u}{t}[/tex]Substituting all known values,
[tex]\begin{gathered} a=\frac{(12\text{ m/s})-0}{(6.0\text{ s})} \\ =2\text{ m/s}^2 \end{gathered}[/tex]Therefore, the acceleration of the runner is 2 m/s².
I am unsure of how to get the answer for this question. Please help!
Answers
ANSWER:
c) 5.4
STEP-BY-STEP EXPLANATION:
Given:
u = 54 km/h
v = 32 km/h
d = 65 m = 0.065 km
We can calculate the time starting from the following equation:
[tex]d=\mleft(\frac{u+v}{2}\mright)\cdot\: t[/tex]We solve for t:
[tex]t=\frac{d}{\mleft(\frac{u+v}{2}\mright)}[/tex]We substitute and calculate the time in hours, then convert that time to seconds, just like this:
[tex]\begin{gathered} t=\frac{0.065}{\frac{54+32}{2}}=0.00151\text{ h} \\ t=0.00151\text{ h}\cdot\frac{3600\text{ sec}}{1\text{ h}} \\ t=5.4\text{ sec} \end{gathered}[/tex]Therefore, the time it would take is 5.4 seconds
A hiker walks 16.19 m at 18.99 degrees. What is the Y component of hisdisplacement?
Answers
Given:
Distance = 16.9 m
θ = 18.99 degrees.
Let's find the Y component of his displacement.
To find the y-component of his displacement, apply the formula:
[tex]F_y=d\sin \theta[/tex]Hence, to find the y-component of his displacement, substitute values into the formula.
Thus, we have:
[tex]F_y=16.19\sin 18.99[/tex]Solving further:
[tex]F_y=5.27\text{ m}[/tex]Therefore, the Y component of his displacement is 5.27 m
ANSWER:
5.27 m
REMOTE GR 8 SCIENCE / SECTION1 / 9 OF 50Which transformation must occur when a dam uses water to generate energy?O A. Mechanical energy to potential energyоB. Chemical energy to potential energyC. Mechanical energy to electrical energyOD. Chemical energy to electrical energy
Answers
As water flows through the dam, its kinetic energy is used to turn a turbine, a generator convert's the turbine mechanical energy into electrical energy.
C. Mechanical energy to electrical energy
A 230-g mass hangs from a string that is wrapped around a pulley, as shown in the figure. The pulley is suspended in such a way that it can rotate freely. When the mass is released, it accelerates toward the floor as the string unwinds. Model the pulley as a uniform solid cylinder of mass 1.00 kg and radius 5.00 cm. Assume that the thread has negligible mass and does not slip or stretch as it unwinds.
Determine the magnitude of the pulley's angular acceleration.
Determine the magnitude of the acceleration of the descending weight.
Calculate the magnitude of the tension in the string.
Answers
The 230-g mass hanging from the 5.00 cm, 1.00 kg pulley and later accelerating as the string unwinds indicates that the parameters of the forces on the mass and pulley are as follows;
The angular acceleration of the pulley is approximately 61.8 m/s²The magnitude of the acceleration of the weight is approximately 3.09 m/s²The tension in the string is approximately 1.5456 NWhat is an angular acceleration of a rotating body?Angular acceleration is the rate at which angular velocity changes with time.
Mass attached to the pulley string, M = 230-g = 0.23 kg
Mass of the pulley, m = 1.00 kg
Radius of the pulley = 5.00 cm = 0.05 m
The equations that can be used are;
a = r·αT·r = I·αm·g - T = m·av = ω·rWhere;
a = The acceleration of the weight
α = The angular acceleration of the pulley
m = Mass of the attached weight
T = The tension in the string
v = The linear velocity
ω = The angular velocity of the pulley
Moment of inertia of the pulley, I = M·r²/2
Therefore, T = ((M·r²/2)/r) × (a/r) = M·a/2
m·g - M·a/2 = m·a
m·g = M·a/2 + m·a = a·(m + M/2)
a = m·g/(m + M/2)
The acceleration of the weight, a = 0.23 × 9.81/(0.23 + 1/2) ≈ 3.09
The acceleration of the weight, a ≈ 3.09 m²/sThe angular acceleration of the pulley, α = a/r
Therefore;
The angular acceleration of the pulley, α = 3.09/0.05 ≈ 61.8 m²/sThe tension in the string, T = m·g - m·a
Therefore;
T = 0.23 × 9.81 - 0.23 × 3.09 = 1.5456
The tension in the string, T ≈ 1.5456 NLearn more about the moment of inertia of a rotating body here:
https://brainly.com/question/14048272
#SPJ1
Which two notes are not an octave apart?1) 256 Hz and 512 Hz2) 262 Hz and 524 Hz3) 331 Hz and 622 Hz4) 277 Hz and 554 Hz
Answers
ANSWER
Option 3
EXPLANATION
Two notes are said to be an octave apart when the frequency of one note is exactly 2 times the other. In other words, it has twice as many waves.
Let us calculate the ratio of each option:
[tex]\begin{gathered} \Rightarrow\frac{512}{256}=2 \\ \Rightarrow\frac{524}{262}=2 \\ \Rightarrow\frac{622}{331}=1.88 \\ \Rightarrow\frac{554}{277}=2 \end{gathered}[/tex]As we can see, only in option 3 is the higher frequency not exactly 2 times the lower frequency.
Therefore, the answer is option 3.
In a dart gun, a spring with k = 400.0 N/m is compressed 8.0 cm when the dart (mass m = 20.0 g) is loaded.
(a) What is the muzzle speed of the dart when the spring is released? Ignore friction.
(b) If the dart gun is located on a table top 2.2 m above the ground, and once the spring is released, it remains compressed by 4 cm, what is the final speed of the dart as it hits the ground?
Answers
The muzzle speed of the dart when the spring is released is 11.3 m/s
The given parameters are
k = spring constant = 400 N/m
m = mass = 20 g = 0.02 kg
Compression = x = 8 cm = 0.08 m
According to the question,
When the dart is loaded, the potential energy is converted into kinetic energy.
Potential Energy (P.E.)
[tex]P.E. =\frac{1}{2} kx^{2}[/tex]
Putting the values,
[tex]P.E. =\frac{1}{2} *400*(0.08)^{2} = 1.28[/tex]
Now, Kinetic Energy (K.E.)
K. E. = [tex]\frac{1}{2} mv^{2}[/tex] = [tex]\frac{1}{2} *0.02*v^{2}= 0.01 v^{2}[/tex]
Now, P.E. = K.E.
[tex]0.01 v^{2} = 1.28 \\\\v^{2} =\frac{1.28}{0.01} \\\\v^{2} = 128\\ \\v = 11.3[/tex]
Hence, the muzzle speed of the dart when the spring is released is 11.3 m/s
To read more about speed, visit https://brainly.com/question/28224010
#SPJ1
A 51-cm-diameter wheel accelerates uniformly about its center from 150 rpm to 290 rpm in 4.0 s.(A) Determine it's angular acceleration. (B) Determine the radial component of the linear acceleration of a point on the edge of the wheel 1.1 s after it has started accelerating. (C) Determine the tangential component of the linear acceleration of a point on the edge of a wheel 1.1 s after it has started accelerating.
Answers
Answer:
(A) 7/6 pi /s^2
(B) 4.145 m/s^2
(C) 119pi/200 m/s^2
Explanation:
Part A.
The angular acceleration is given by
[tex]\alpha=\frac{\omega_f-\omega_i}{\Delta t}[/tex]where wf is the initial angular velocity and wi is the final angular velocity and t is the time interval.
Now, we are given the angular velocity is given in rpm and we have to convert it into radians/sec .
150 rpm = 150 x 2pi / 60 min = 5 pi rad/ sec
290 rpm = 290 x 2pi / 60 min = 29/ 3 pi rad/ sec
Now we are in the position to find the angular acceleration
[tex]\alpha=\frac{\frac{29}{3}\pi-5\pi}{4s-0s}[/tex][tex]\boxed{\alpha=\frac{7}{6}\pi\; /s^2}[/tex]which is our answer!
Part B.
The radial acceleration is given by
[tex]a_r=\frac{v^2}{R}[/tex]where v is the velocity of the object (moving in a circle) and R is the radius of the circle.
Now,
[tex]v=\alpha Rt[/tex]putting in the values of alpha, R and t = 1.1 s gives
[tex]v=\frac{7}{6}\pi\times\frac{0.51}{2}\times1.1[/tex][tex]v=1.028\; m/s[/tex]therefore,
[tex]a_r=\frac{v^2}{R}=\frac{(1.028)^2}{0.51/2}[/tex][tex]\boxed{a_r=4.145/s^2}[/tex]which is our answer!
Part C.
Here we have to relationship between angular and tangential acceleration:
[tex]a=\alpha R[/tex]where r is the radius of the circle.
Since R = 0.51/2 m, we have
[tex]a=\frac{7}{6}\pi\cdot\frac{0.51}{2}m[/tex][tex]\boxed{a=\frac{119}{400}\pi}[/tex]which is our answer!
Hence, to summerise
(A) 7/6 pi /s^2
(B) 4.145 m/s^2
(C) 119pi/200 m/s^2
Uncle Harry weighs 75 N. What would his mass be in kilograms?
Answers
Uncle Harry's mass is 7.5 kg.
The weight of a body is defined as the gravitational force with which a body is attracted toward the center of the earth.
If [tex]g[/tex] is the acceleration due to gravity at a place, then a body of mass [tex]m[/tex] is attracted towards the center of the earth with a force equal to [tex]mg[/tex] at the place. Whereas, the mass of a body remains the same everywhere.
Hence the weight of a body is given by
[tex]W = mg[/tex] -------------- (1)
As the value of [tex]g[/tex] varies from place to place, the weight of a body also varies from place to place.
Given that, the weight of Uncle Harry, [tex]W=[/tex] [tex]75 N.[/tex]
From equation (1), we get mass as,
[tex]m=\frac{W}{g}[/tex] --------------(2)
Taking acceleration due to gravity, [tex]g= 10 m/s^{2}[/tex],.
Substitute for [tex]W[/tex] and [tex]g[/tex] in equation (2), we have,
[tex]m=\frac{75}{10}\\ \\m=7.5 kg[/tex]
Thus, the mass of Uncle Harry is [tex]7.5 kilograms.[/tex]
To read more about weight and mass visit:
https://brainly.com/question/1384116
A 5.0g bullet is fired straight up from the ground, The bullet leaves the ground with a speed of 85 m/s taking to the ground as the reference levelA) what is the gravitational P.E of the bulletB) what is the initial KE of the bulletC) what is the total initial ME of the bullet when the bullet is 12m high above the groundD) what is the gravitational PE of the bulletE) what should the ME be at this height F) how fast is the bullet moving at this height
Answers
Given information:
Mass of the bullet;
[tex]\begin{gathered} m=5\text{ g} \\ =5\times10^{-3}\text{ kg} \end{gathered}[/tex]Initial velocity of the bullet;
[tex]u=85\text{ m/s}[/tex]Part (a),
Taking ground as the reference level. So, the initial height of the bullet is 0 m.
The gravitational potential energy is given as,
[tex]U=\text{mgh}[/tex]Here, g is the acceleration due to gravity.
Substituting all known values,
[tex]\begin{gathered} U=(5\times10^{-3}\text{ kg})\times(9.8\text{ m/s}^2)\times0 \\ =0\text{ J} \end{gathered}[/tex]Therefore, the gravitational potential energy at the ground is 0 J.
Part (B)
The initial kinetic energy of the bullet is given as,
[tex]K=\frac{1}{2}mu^2[/tex]Substituting all known values,
[tex]\begin{gathered} K=\frac{1}{2}\times(5\times10^{-3}\text{ kg})\times(85\text{ m/s})^2 \\ =18.0625\text{ J} \end{gathered}[/tex]Therefore, the initial kinetic energy of the bullet is 18.0625 J.
Part (C).
According to the conservation of energy, the total mechanical energy (ME) of the bullet will remain conserved. Therefore, the total initial ME of the bullet when the bullet is 12 m high above the ground is 18.0625 J.
Part (D)
The gravitational potential energy when the bullet is 12 m high is,
[tex]U_h=mgh[/tex]Substituting all known values,
[tex]\begin{gathered} U_h=(5\times10^{-3})\times(9.8\text{ m/s}^2)\times(12\text{ m}) \\ =0.588\text{ J} \end{gathered}[/tex]Therefore, the gravitational potential energy when the bullet is 12 m high is 0.588 J.
Part (E).
The velocity of the bullet when it reaches the height of 12 m is given as,
[tex]v^2=u^2-2gh[/tex]Here, v is the velocity when the bullet is 12 m high.
Substituting all known values,
[tex]\begin{gathered} v^2=(85\text{ m/s})^2-2\times(9.8\text{ m/s})\times(12\text{ m}) \\ =6989.8\text{ m}^2\text{ /s}^2 \end{gathered}[/tex]The total mechanical energy when the bullet is 12 m high is,
[tex]ME=U_h+\frac{1}{2}mv^2[/tex]Substituting all known values,
[tex]\begin{gathered} ME=(0.588\text{ J})+\frac{1}{2}\times(5\times10^{-3}\text{ kg})\times(6989.8\text{ m}^2\text{ /s}^2) \\ =18.0625\text{ J} \end{gathered}[/tex]Therefore, the total mechanical energy ME when the bullet is 12 m high is 18.0625 J.
Part (F),
The velocity when the bullet is 12 m high is given as,
[tex]v=\sqrt[]{u^2-2gh}[/tex]Substituting all known values,
[tex]\begin{gathered} v=\sqrt[]{(85\text{ m/s})^2-2\times(9.8\text{ m/s}^2)\times(12\text{ m})} \\ \approx83.605\text{ m/s} \end{gathered}[/tex]Therefore, the velocity when the bullet is 12 m high is 83.605 m/s.
A 0.86 m tall object is placed 3.35 m away from a lens. If the image is 4.58 m tall, how far away from the lens was the image produced? O
Answers
The magnification is the ratio of the image size to the object size. If the image and object are in the same medium, it is just the image distance divided by the object distance:
[tex]M=\frac{i}{o}[/tex]On the other hand:
[tex]M=\frac{h^{\prime}}{h}[/tex]Where h' is the size of the image and h is the size of the object.
Therefore:
[tex]\frac{h^{\prime}}{h}=\frac{i}{o}[/tex]Substitute h'=4.58m, h=0.86m and o=3.35m to find i, the distance from the lens at which the image is produced:
[tex]\begin{gathered} \Rightarrow i=\frac{h^{\prime}}{h}\cdot o \\ =\frac{4.58m}{0.86m}\cdot3.35m \\ =17.84m \end{gathered}[/tex]Therefore, the image is produced 17.84m away from the lens.
An object weighing 88 N is pushed by a 100 N force. What is the acceleration of the object?
Answers
Given data:
* The weight of the object is 88 N.
* The force acting on the object is 100 N.
Solution:
The weight of the object in terms of the mass of the object is,
[tex]W=mg[/tex]where m is the mass of the object, and g is the acceleration due to gravity,
Substituting the known values,
[tex]\begin{gathered} 88=m\times9.8 \\ m=\frac{88}{9.8} \\ m=8.98\text{ kg} \end{gathered}[/tex]According to Newton's second law, the acceleration of the object in terms of the force acting on the object is,
[tex]F=ma[/tex]where a is the acceleration of the object,
Substituting the known values,
[tex]\begin{gathered} 100=8.98\times a \\ a=\frac{100}{8.98} \\ a=11.14ms^{-2} \end{gathered}[/tex]Thus, the acceleration of the object is 11.14 meters per second squared.
Two positive charge spheres, the spheres are separated by 0.40 m. The charge on the first sphere is 100 microcoulombs and the
charge on the second sphere has 30 microcoulombs. Calculate the Electric Force on the charges?
Answers
Answer: 168.75 N
Explanation:
first, let's convert microcoulombs to coulombs
q1 = 1e-4 C
q2 = 3e-5 C
r = 0.4 m
then use the equation Fe = [tex]\frac{kq_{1} q_{2}}{r^{2} }[/tex]
plug in values --> F = (9e9*1e-4*3e-5)/(0.4)^2
F = 168.75 N
Describe what values you could solve for if you were given kinetic energy?
Answers
The kinetic energy is given by:
[tex]K=\frac{1}{2}mv^2[/tex]From the above equation,
we can solve from the mass m if velocity is given
or for the velocity if mass m is given
Explain the relation between the period and the other variable below in spring, show your point using formula.
Answers
Explanation:
The period in spring can be calculated as
[tex]T=2\pi\sqrt{\frac{m}{k}}[/tex]Where m is the mass attached and k is the spring constant.
Answer:
Taking into account this formula, we can conclude the following:
- Period vs. Stretch distance.
The formula doesn't include the stretch distance, so the period is independent of the stretch distance. No matter what is the stretch distance the period will not change.
- Period vs. Mass attached
The period is proportional to the square root of the mass, so when the mass is greater the period is greater.
-Period vs. Spring constant
The period is inversely proportional to the square root of the spring constant, so when the spring constant increases, the period decreases.
An eagle goes straight up with an initial velocity of 75m/s toward its food. Its food is located 250m above the ground. How fast will the eagle be moving when she reaches her food?
Answers
The vertical distance covered by the eagle can be given as,
[tex]h=ut+\frac{1}{2}gt^2[/tex]Plug in the known values,
[tex]\begin{gathered} 250m=(75\text{ m/s)t+}\frac{1}{2}(-9.8m/s^2)t^2 \\ -(4.90ms^{-2})t^2+(75\text{ m/s)t-250m=0} \\ (4.90ms^{-2})t^2-(75\text{ m/s)t+250 m=0} \end{gathered}[/tex]The above equation can be further solved as,
[tex]\begin{gathered} t=\frac{75\text{ m/s}\pm\sqrt[]{(75m/s)^2-4(4.90ms^{-2})(250\text{ m)}}}{2(4.90ms^{-2})^{}} \\ =\frac{75\text{ m/s}\pm26.9\text{ m/s}}{9.80m/s^2} \\ =10.4\text{ s, }4.91\text{ s} \end{gathered}[/tex]Therefore, the time taken by eagle to reach at food is 10.4 s or 4.91 s.
An athlete swings a 7.9 kg ball horizontally on the end of a rope. The ball moves in a circle of radius 0.9 m at an angular speed of 0.27 rev/s.
Answers
The tangential velocity of the ball will be 1.53 m/s
What is tangential velocity?Tangential velocity is the linear component of an object's velocity moving along a circular path. If an object moves in a circular orbit with a distance r from the center, the object's velocity is always directed tangentially. This is called tangential velocity. Any instantaneous linear velocity is also said to be its tangential velocity.
The rate of change of the object's angular displacement is the angular velocity. It is represented by ω and its standard unit is radians/second. It differs from linear velocity as it only deals with objects moving in circular motion. So we measure the speed at which the angular displacement is swept.
Tangential speed = angular speed × radius of the circle
[tex]V_{t}[/tex] = r×ω
For the given case,
Radius (r) = 0.9 m
Angular speed (ω) = 0.27 rev/sec = 1.70 rad/sec
tangential speed ([tex]V_{t}[/tex]) = 0.9 × 1.70 = 1.53 m/s
To know more about tangential velocity visit:
https://brainly.com/question/28738284
#SPJ4
"An athlete swings a 7.9 kg ball horizontally on the end of a rope. The ball moves in a circle of radius 0.9 m at an angular speed of 0.27 rev/s. What is the tangential velocity of ball?"
Unpolarized light with intensity 455.16 W/m2 passes first through a polarizing filter with its axis vertical, then through a polarizing filter with its axis 33.33o from vertical. What light intensity emerges from the second filter ?
Answers
Given:
The intensity of unpolarized incident light is
[tex]I_0=455.16\text{ W/m}^2[/tex]It passes first through a polarizing filter with its axis vertical
The second polarising filter is at an angle of,
[tex]\theta=33.33\degree[/tex]from the vertical
To find:
What light intensity emerges from the second filter ?
Explanation:
According to the Malus law, the emergent light intensity is,
[tex]\begin{gathered} I=I_0cos^2\theta \\ =455.16\times cos^233.33\degree \\ =317.74\text{ W/m}^2 \end{gathered}[/tex]Hence, the required intensity is
[tex]317.74\text{ W/m}^2[/tex]Coulomb's Law equation is: FE = kq1q2/r2In this expression, FE is the electric force between charges q1 and q2 separated by distance r.When the signs of the charges are included for q1 and q2 , the evaluation of Coulomb's Law equation can yield a positive or negative answer for FE .What is the appropriate interpretation of the sign of the numeric evaluation of FE ?(A) If FE is negative, the charges are attracting.(B) If FE is positive, the charges are attracting.
Answers
We know like charges repel amd unlike charges attract.
Thus if one charge is positive and other is negative then both charges will attract each other.
So if the force is negative , the charges are attracting.
Thus the answer is:
(A) If FE is negative, the charges are attracting.
In the summer time fruit flies are the worst. One morning I woke up to 5 fruit flies in my kitchen. Three hours later there were 13 fruit flies. If the growth rate is continuous, at what rate are the flies increasing? Round answers to four decimal places.
Answers
We are asked to determine the continuous growth rate. To do that we will use the following function:
[tex]P(t)=P_0e^{kt}[/tex]Where "P0" is the initial population, "k" is the growth rate, and "t" is time. Replacing the initial population of 5 we get:
[tex]P(t)=5e^{kt}[/tex]Now we are told that the population is 13 when the time is 3 hours. Replacing we get:
[tex]13=5e^{3k}[/tex]Now we solve for "k". First, by dividing both sides by 5:
[tex]\frac{13}{5}=e^{3k}[/tex]Now we take natural logarithm to both sides:
[tex]\ln (\frac{13}{5})=\ln (e^{3k})[/tex]Now we use the following property of logarithms:
[tex]\ln x^y=y\ln x[/tex]Applying the property:
[tex]\ln (\frac{13}{5})=3k\ln e[/tex]We have that the value of ln(e) is 1, therefore:
[tex]\ln (\frac{13}{5})=3k[/tex]Now we divide both sides by 3:
[tex]\frac{1}{3}\ln (\frac{13}{5})=k[/tex]Solving the operation we get:
[tex]0.319=k[/tex]Therefore, the growth rate is 0.319.
An ocean wave usually occurs at a frequency of 2.0 hz what is the period of each wave?
Answers
The period of a wave can be calculated with the formula below:
[tex]T=\frac{1}{f}[/tex]Where f is the frequency.
If the frequency is 2 Hz, the period is:
[tex]T=\frac{1}{2}=0.5\text{ s}[/tex]Therefore the period is 0.5 seconds.
6 identical books are lying on a desktop. a tidy student decides to stack the books one on top of the other. if students do 11 J of work width of the spine of each book is 2.5 what is the mass
Answers
Before an impact, object 1 has a momentum of 25 kg m/s straight north and object 2 has amomentum of 75 kg m/s straight south. What is the total momentum after the impact?
Answers
Answer:
50 kg m/s straight south.
Explanation:
By the conservation of momentum, the total momentum after the impact is equal to the momentum before the impact. Since the objects have momentum in opposite directions, we need to subtract the values, so
[tex]\begin{gathered} p=75\text{ kg m/s - 25 kg m/s} \\ p=50\text{ kg m/s} \end{gathered}[/tex]Therefore, the total momentum after the impact is 50 kg m/s straight south.
Select all of the following that are equal to an impulse of 30 units.
A. Force = 30, time = 1.2
B. Force = 0.1, time = 300
I C. Force = 6, time = 4
D. Force = 10, time = 3
Answers
ANSWER
B and D
EXPLANATION
The impulse is the product of the force applied to an object and the amount of time the force is applied
[tex]\Delta p=F\cdot\Delta t[/tex]Let's find the impulse with the information on each option.
A. F = 30, Δt = 1.2
[tex]\Delta p=30\cdot1.2=36[/tex]B. F = 0.1, Δt = 300
[tex]\Delta p=0.1\cdot300=30[/tex]C. F = 6, Δt = 4
[tex]\Delta p=6\cdot4=24[/tex]D. F = 10, Δt = 3
[tex]\Delta p=10\cdot3=30[/tex]The options that have an impulse equal to 30 are B and D
3. What are the charges and location of each of the parts of the atom?
Answers
There are two parts main parts of the atoms they are the nucleus and the orbits.
The atom mains consists of three particles, protons, neutrons, and electrons.
The protons are positively charged particles. The charge of a proton is 1.602×10⁻¹⁹ C. And the neutron does not possess any charge. The neutrons are neutral particles. Protons and neutrons are located at the nucleus of an atom.
The electrons are negatively charged particles. The charge of an electron is -1.602×10⁻¹⁹ C. The electrons will be orbiting the nucleus. Thus they are located around the nucleus of an atom.
a radio station broadcast a program at 128.7 Mhz. calculate the wavelength of the radiowave at this frequency
Answers
The wavelength of the radio wave is 2.33 meters.
Given that the frequency of the radio wave is 128.7MHz.
[tex]128 MHz = 128 * 10^{6} Hz[/tex]
Radio waves are electromagnetic waves. All electromagnetic waves (including radio waves ) travel at a speed [tex](c)[/tex] of [tex]3*10^{8} m/s[/tex].
The speed of the radio wave is given by speed = frequency*wavelength.
Hence, the wavelength of the radio wave can be calculated as,
[tex]wavelength = \frac{speed}{frequency}[/tex]
Thus, [tex]wavelength = \frac{3*10^{8} }{128.7*10^{6} } meters.[/tex]
[tex]=2.33 meters.[/tex]
Hence, the wavelength of the radio wave is [tex]2.33 meters.[/tex]
To read a similar problem on radio waves visit:
https://brainly.com/question/23136889
A 120 kg car accelerates from initial speed 5.0 m/s to final speed 10.0 m/s in 5.0 seconds. How much power (watts) does that require?
Answers
In order to determine the required power, use the following formula:
[tex]P=\frac{W}{t}[/tex]where
t: time = 5.0 s
W: work
calculate the work W as follow:
[tex]W=F\cdot d=m\cdot a\cdot d[/tex]where
m: mass = 120 kg
a: acceleration = ?
d: distance
calculate the acceleration as follow:
[tex]a=\frac{v-v_0}{t}=\frac{10.0\text{ m/s- 5.0m/s}}{5.0s}=1\frac{m}{s^2}[/tex]the distance can be obtained by using the following formula:
[tex]d=v_0\cdot t+\frac{1}{2}at^2=(\frac{5.0m}{s})(5.0s)+\frac{1}{2}(\frac{1m}{s^2})(5.0s)^2=37.5m[/tex]then, replace the previous values of a and d to calculate W:
[tex]W=(120kg)(\frac{1m}{s^2})(37.5m)=4500J[/tex]Finally, replace W and d into the formual for the power P:
[tex]P=\frac{4500J}{5.0s}=900W[/tex]Hence, 900 watts are required to accelerate the car.
A net constant force of 1500 N gives a toy rocket an acceleration of 2.5 m/s squared. what is the the mass of the rocket?
Answers
We have
F=1500N
a=2.5 m/s^2
We use the next formula
[tex]F=ma[/tex]Where F is the force, m is the mass and a is the acceleration
Then we substitute
[tex]1500=2.5\text{ m}[/tex]Then we isolate the m
[tex]m=\frac{1500}{2.5}=600kg[/tex]ANSWER
the mass of the rocket is 600kg
Explain why force, acceleration, and velocity are vectors.
Answers
Answer:
simply because they all have direction
Explanation:
vector quantities are quantities which have both magnitude and direction.Force,acceleration and velocity have both magnitude and direction.