Answers
Answer:
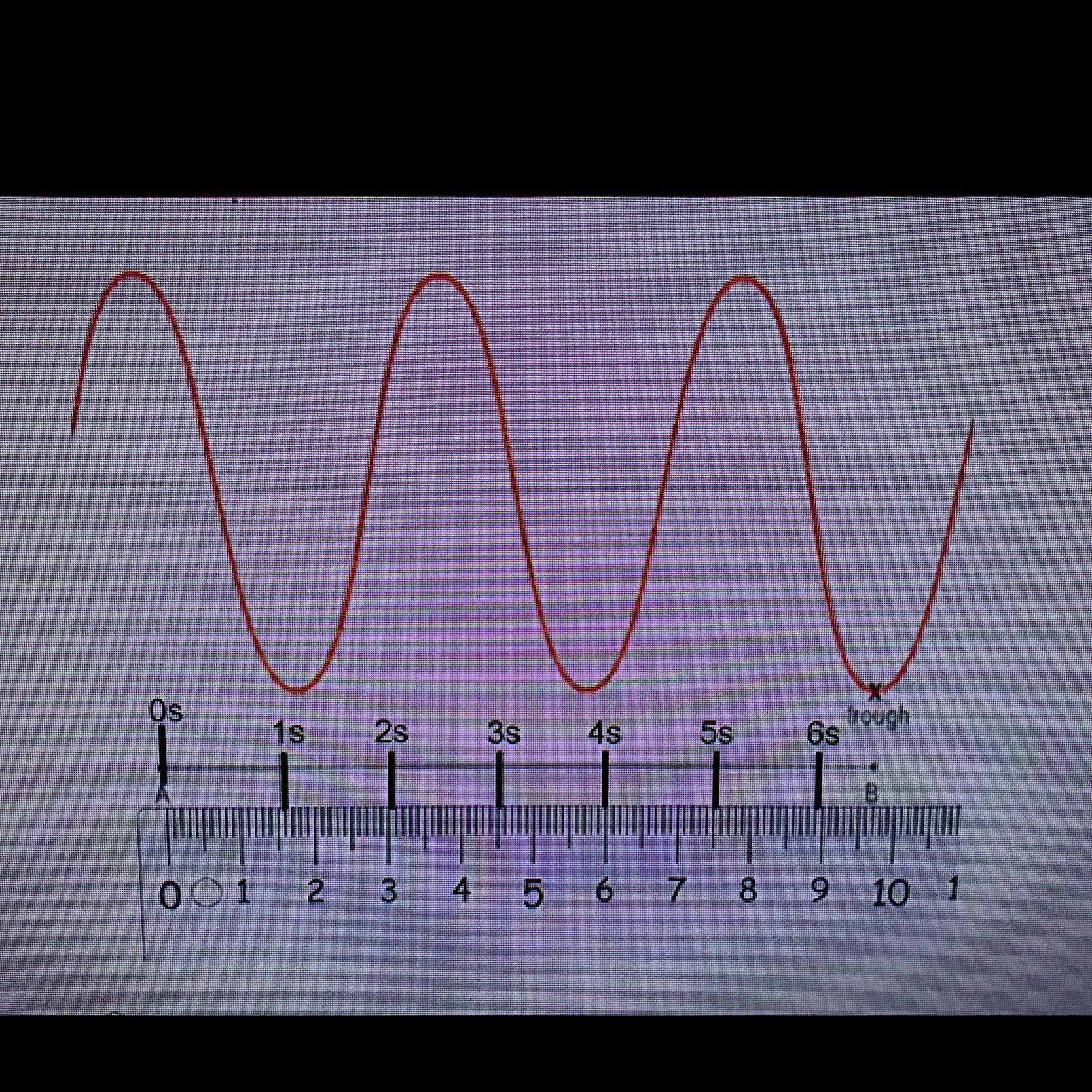
2.5 seconds
Explanation:
Perios is time divided by number of oscilliations. From the diagram the number of oscilliations is two. This can be seen by counting successive crests of the wave from the 0s mark. The 2 oscilliatoions ends in 5s. 5 divided by 2 is 2.5s.
Related Questions
Uncle Harry weighs 75 N. What would his mass be in kilograms?
Answers
Uncle Harry's mass is 7.5 kg.
The weight of a body is defined as the gravitational force with which a body is attracted toward the center of the earth.
If [tex]g[/tex] is the acceleration due to gravity at a place, then a body of mass [tex]m[/tex] is attracted towards the center of the earth with a force equal to [tex]mg[/tex] at the place. Whereas, the mass of a body remains the same everywhere.
Hence the weight of a body is given by
[tex]W = mg[/tex] -------------- (1)
As the value of [tex]g[/tex] varies from place to place, the weight of a body also varies from place to place.
Given that, the weight of Uncle Harry, [tex]W=[/tex] [tex]75 N.[/tex]
From equation (1), we get mass as,
[tex]m=\frac{W}{g}[/tex] --------------(2)
Taking acceleration due to gravity, [tex]g= 10 m/s^{2}[/tex],.
Substitute for [tex]W[/tex] and [tex]g[/tex] in equation (2), we have,
[tex]m=\frac{75}{10}\\ \\m=7.5 kg[/tex]
Thus, the mass of Uncle Harry is [tex]7.5 kilograms.[/tex]
To read more about weight and mass visit:
https://brainly.com/question/1384116
Object A has a mass of 3 kg and a velocity of 2 m/s. It collides and sticks to object B which had a mass of 10 kg and a velocity of 1 m/s. How fast will the object AB be moving after the collision?
Answers
Object AB is moving with the velocity of 1.23 m/s.
Givne data:
The mass of object A is m=3 kg.
The velocity of object A is u=2 m/s.
The mass of object B is M=10 kg
The velocity of object B is v=1 m/s.
Applying the conservation of momentum before and after the collision,
[tex]\begin{gathered} mu+Mv=(m+M)V \\ (3)(2)+(10)(1)=(3+10)V \\ V=1.23\text{ m/s} \end{gathered}[/tex]Thus, the object AB moving with a velocity of 1.23 m/s after the collision.
Explain why force, acceleration, and velocity are vectors.
Answers
Answer:
simply because they all have direction
Explanation:
vector quantities are quantities which have both magnitude and direction.Force,acceleration and velocity have both magnitude and direction.
A 51-cm-diameter wheel accelerates uniformly about its center from 150 rpm to 290 rpm in 4.0 s.(A) Determine it's angular acceleration. (B) Determine the radial component of the linear acceleration of a point on the edge of the wheel 1.1 s after it has started accelerating. (C) Determine the tangential component of the linear acceleration of a point on the edge of a wheel 1.1 s after it has started accelerating.
Answers
Answer:
(A) 7/6 pi /s^2
(B) 4.145 m/s^2
(C) 119pi/200 m/s^2
Explanation:
Part A.
The angular acceleration is given by
[tex]\alpha=\frac{\omega_f-\omega_i}{\Delta t}[/tex]where wf is the initial angular velocity and wi is the final angular velocity and t is the time interval.
Now, we are given the angular velocity is given in rpm and we have to convert it into radians/sec .
150 rpm = 150 x 2pi / 60 min = 5 pi rad/ sec
290 rpm = 290 x 2pi / 60 min = 29/ 3 pi rad/ sec
Now we are in the position to find the angular acceleration
[tex]\alpha=\frac{\frac{29}{3}\pi-5\pi}{4s-0s}[/tex][tex]\boxed{\alpha=\frac{7}{6}\pi\; /s^2}[/tex]which is our answer!
Part B.
The radial acceleration is given by
[tex]a_r=\frac{v^2}{R}[/tex]where v is the velocity of the object (moving in a circle) and R is the radius of the circle.
Now,
[tex]v=\alpha Rt[/tex]putting in the values of alpha, R and t = 1.1 s gives
[tex]v=\frac{7}{6}\pi\times\frac{0.51}{2}\times1.1[/tex][tex]v=1.028\; m/s[/tex]therefore,
[tex]a_r=\frac{v^2}{R}=\frac{(1.028)^2}{0.51/2}[/tex][tex]\boxed{a_r=4.145/s^2}[/tex]which is our answer!
Part C.
Here we have to relationship between angular and tangential acceleration:
[tex]a=\alpha R[/tex]where r is the radius of the circle.
Since R = 0.51/2 m, we have
[tex]a=\frac{7}{6}\pi\cdot\frac{0.51}{2}m[/tex][tex]\boxed{a=\frac{119}{400}\pi}[/tex]which is our answer!
Hence, to summerise
(A) 7/6 pi /s^2
(B) 4.145 m/s^2
(C) 119pi/200 m/s^2
Explain the relation between the period and the other variable below in spring, show your point using formula.
Answers
Explanation:
The period in spring can be calculated as
[tex]T=2\pi\sqrt{\frac{m}{k}}[/tex]Where m is the mass attached and k is the spring constant.
Answer:
Taking into account this formula, we can conclude the following:
- Period vs. Stretch distance.
The formula doesn't include the stretch distance, so the period is independent of the stretch distance. No matter what is the stretch distance the period will not change.
- Period vs. Mass attached
The period is proportional to the square root of the mass, so when the mass is greater the period is greater.
-Period vs. Spring constant
The period is inversely proportional to the square root of the spring constant, so when the spring constant increases, the period decreases.
Layla was hiking in the Grand Canyon with her best friend Saige. The temperature when they started gut was only 4.0° C. She shouted at the canyon wall and 2.8 s later she heard her own voice echoing back. How far away was the canyon wall? a) 4.6 x 10² m b) 46.6 m c) 47 m d) 466.7 m
Answers
Given:
The temperature of the surrounding is 4 degrees Celsius.
The time taken for the echo to reach the ears is t = 2.8 s
Required:
The distance from the canyon wall.
Explanation:
The distance traveled by the sound is 2d as it travels up to the wall and bounces back.
The distance can be calculated by the formula
[tex]d=\frac{v\times t}{2}[/tex]Here, the speed of sound at 4 degrees Celsius is
[tex]v=331.3\text{ m/s}[/tex]On substituting the values, the distance traveled will be
[tex]\begin{gathered} d=\frac{331.3\times2.8}{2} \\ =4.6\times10^2\text{ m} \end{gathered}[/tex]Final Answer: The distance traveled is 4.6 x 10^2 m
Which of the following representsthis number in standard notation?5.05 · 104A. 50500B. 5050C. 0.000505D. 0.0505
Answers
The number is denoted in standard notation is as follows:
[tex]\begin{gathered} Y=5.05\times10^4 \\ Y=5.05\times10000 \\ Y=50500 \end{gathered}[/tex]Thus, the standard notation of this number is 50500.
Thus, the correct option for the above question is A.
Before an impact, object 1 has a momentum of 25 kg m/s straight north and object 2 has amomentum of 75 kg m/s straight south. What is the total momentum after the impact?
Answers
Answer:
50 kg m/s straight south.
Explanation:
By the conservation of momentum, the total momentum after the impact is equal to the momentum before the impact. Since the objects have momentum in opposite directions, we need to subtract the values, so
[tex]\begin{gathered} p=75\text{ kg m/s - 25 kg m/s} \\ p=50\text{ kg m/s} \end{gathered}[/tex]Therefore, the total momentum after the impact is 50 kg m/s straight south.
How do I do this problem? 9.A) A 100 g apple is falling from a tree. What is the impulse that Earth exerts on it during the first 0.5s ofits fall? What about the next 0.5 s?9.B) The same 100 g apple is falling from the tree. What is the impulse that Earth exerts on it in the first0.5 m of its fall? What about the second 0.5 m?9.c) Give a clear explanation for why the answers from 9.a and 9.b are different.
Answers
Given:
The mass of the apple is m = 100g = 0.1 kg
To find (A) the impulse during the first 0.5 s and in the next 0.5 s
(B) Impulse during the first 0.5 m of its fall and about the second 0.5 m.
(C)
Explanation:
(A) The force acting on the apple will be
[tex]\begin{gathered} F=mg \\ =0.1\times9.8\text{ } \\ =\text{ 0.98 N} \end{gathered}[/tex]Impulse during the first 0.5 s will be
[tex]\begin{gathered} Impulse\text{ = 0.98}\times0.5 \\ =0.49\text{ N s} \end{gathered}[/tex]Impulse during the second 0.5 s will be
[tex]\begin{gathered} Impulse\text{ =0.98}\times(0.5+0.5) \\ =0.98\text{ N s} \end{gathered}[/tex](B) The distance traveled by the apple is d = 0.5 m
[tex]\begin{gathered} d1=\frac{1}{2}g(t1)^2 \\ t1=\sqrt{\frac{2d1}{g}} \\ =\sqrt{\frac{2\times0.5}{9.8}} \\ =0.319\text{ s} \end{gathered}[/tex]The velocity will be
[tex]\begin{gathered} v1=gt1 \\ =9.8\times0.319 \\ =3.1262\text{ m/s} \end{gathered}[/tex]The distance traveled by the apple in the second 0.5 m
[tex]\begin{gathered} d2=\frac{1}{2}g(t2)^2 \\ t2=\sqrt{\frac{2d2}{g}} \\ =\sqrt{\frac{2\times0.5}{9.8}} \\ =0.319\text{ s} \end{gathered}[/tex]The velocity will be
'
[tex]\begin{gathered} v2=v1+gt2 \\ =3.1262+(9.8\times0.319) \\ =6.2524\text{ m/s} \end{gathered}[/tex]The impulse will be
[tex]\begin{gathered} Impulse=\text{ change in momentum} \\ =mv2-mv1 \\ =0.1\times(6.2524)-0.1\times(3.1262) \\ =0.62524-0.31262 \\ =0.31262\text{ N s} \end{gathered}[/tex](C) Although the numerical value is the same in both the cases but in part A it is the time and in part B it is the distance.
Hey there, I have a physics question that sadly I can't figure out since the pearson e book keeps crashing. Also I am blind and CAN'T SEE PICTURES OR GRAPHS!! So for the question: Let θ be the angle that the vector A⃗ makes with the +x-axis, measured counterclockwise from that axis. Find the angle θ for a vector that has the following components.Part AAx= 4.20 m, Ay= -2.10 mExpress your answer in degrees.
Answers
ANSWER:
333.4°
STEP-BY-STEP EXPLANATION:
To find angle for a vector:
[tex]\theta=\tan ^{-1}\mleft(\frac{A_y}{A_x}\mright)[/tex]We substitute the values of this case and the angle would then be:
[tex]\begin{gathered} \theta=\tan ^{-1}\mleft(\frac{-2.10}{4.20}\mright) \\ \theta=\tan ^{-1}(-0.5) \\ \theta=-26.56\cong-26.6 \\ \theta=360-26.6 \\ \theta=333.4\text{\degree} \end{gathered}[/tex]The angle is 333.4°
An escalator is used to move 20 passengers every 60s from the first floor of a department store to the second. The second floor is located above the first floor. The average passenger's mass is 54.9 kg. Determine the power requirement of the escalator in order to move this number of passengers in this amount of time
Answers
From the information given,
The average passenger's mass is 54.9 kg
Force exerted by each passenger = weight of passenger = mg
where
m = mass = 54.9
g = acceleration due to gravity = 9.8m/s^2
Force = weight = 54.9 x 9.8 = 538.02 N
We would determine the work done in moving one passenger. The formula for calculating work is
work = force x distance
distance = 5.2
Work = 538.02 x 5.2 = 2797.704 J
Work done in moving 20 passengers = 2797.704 x 20 = 55954.08
Recall,
Power = work/time
Given that time = 60s,
Power = 55954.08/60
Power = 933 W
the power requirement of the escalator in order to move this number of passengers in this amount of time is 933 W
A wave traveling on a Slinky® that is stretched to 4 m takes 4.97 s to travel the length of the Slinky and back again.(a) What is the speed (in m/s) of the wave? 1.61 m/s b) Using the same Slinky® stretched to the same length, a standing wave is created which consists of seven antinodes and eight nodes. At what frequency (in Hz) must the Slinky be oscillating? Hz =
Answers
Given:
The length of the slinky is: L = 4 m.
The time taken by the wave to travel the length and back again is: t = 4.97 s
To find:
a) The speed of the wave
b) The frequency of the wave
Explanation:
a)
As the wave on the slinky travels along the length and back again, it covers a distance that is double the distance of the slinky.
Thus, the total distance "d" traveled by the wave will be 2L.
The speed "v" of the wave is given as:
[tex]\begin{gathered} v=\frac{d}{t} \\ \\ v=\frac{2L}{t} \end{gathered}[/tex]Substituting the values in the above equation, we get:
[tex]\begin{gathered} v=\frac{2\times4\text{ m}}{4.97\text{ s}} \\ \\ v=\frac{8\text{ m}}{4.97\text{ s}} \\ \\ v=1.61\text{ m/s} \end{gathered}[/tex]Thus, the speed of the wave is 1.61 m/s
b)
The standing wave created consists of seven antinodes and eight nodes. Thus, the length of the slinky is 7/2 times the wavelength of the wave.
[tex]L=\frac{7}{2}\lambda[/tex]Rearranging the above equation, we get:
[tex]\lambda=\frac{2}{7}L[/tex]Substituting the values in the above equation, we get:
[tex]\lambda=\frac{2}{7}\times4\text{ m}=\frac{8\text{ m}}{7}=1.143\text{ m}[/tex]The speed "v" of the wave is related to its wavelength "λ" and a frequency "f" as:
[tex]v=f\lambda[/tex]Rearranging the above equation, we get:
[tex]f=\frac{v}{\lambda}[/tex]Substituting the values in the above equation, we get:
[tex]\begin{gathered} f=\frac{1.61\text{ m/s}}{1.143\text{ m}} \\ \\ f=1.41\text{ Hz} \end{gathered}[/tex]Thus, the frequency of the wave on the slinky is 1.41 Hz.
Final answer:
a) The speed of the wave is 1.61 m/s.
b) The frequency of the oscillation of the slinky is 1.41 Hz.
A net constant force of 1500 N gives a toy rocket an acceleration of 2.5 m/s squared. what is the the mass of the rocket?
Answers
We have
F=1500N
a=2.5 m/s^2
We use the next formula
[tex]F=ma[/tex]Where F is the force, m is the mass and a is the acceleration
Then we substitute
[tex]1500=2.5\text{ m}[/tex]Then we isolate the m
[tex]m=\frac{1500}{2.5}=600kg[/tex]ANSWER
the mass of the rocket is 600kg
A 5.0g bullet is fired straight up from the ground, The bullet leaves the ground with a speed of 85 m/s taking to the ground as the reference levelA) what is the gravitational P.E of the bulletB) what is the initial KE of the bulletC) what is the total initial ME of the bullet when the bullet is 12m high above the groundD) what is the gravitational PE of the bulletE) what should the ME be at this height F) how fast is the bullet moving at this height
Answers
Given information:
Mass of the bullet;
[tex]\begin{gathered} m=5\text{ g} \\ =5\times10^{-3}\text{ kg} \end{gathered}[/tex]Initial velocity of the bullet;
[tex]u=85\text{ m/s}[/tex]Part (a),
Taking ground as the reference level. So, the initial height of the bullet is 0 m.
The gravitational potential energy is given as,
[tex]U=\text{mgh}[/tex]Here, g is the acceleration due to gravity.
Substituting all known values,
[tex]\begin{gathered} U=(5\times10^{-3}\text{ kg})\times(9.8\text{ m/s}^2)\times0 \\ =0\text{ J} \end{gathered}[/tex]Therefore, the gravitational potential energy at the ground is 0 J.
Part (B)
The initial kinetic energy of the bullet is given as,
[tex]K=\frac{1}{2}mu^2[/tex]Substituting all known values,
[tex]\begin{gathered} K=\frac{1}{2}\times(5\times10^{-3}\text{ kg})\times(85\text{ m/s})^2 \\ =18.0625\text{ J} \end{gathered}[/tex]Therefore, the initial kinetic energy of the bullet is 18.0625 J.
Part (C).
According to the conservation of energy, the total mechanical energy (ME) of the bullet will remain conserved. Therefore, the total initial ME of the bullet when the bullet is 12 m high above the ground is 18.0625 J.
Part (D)
The gravitational potential energy when the bullet is 12 m high is,
[tex]U_h=mgh[/tex]Substituting all known values,
[tex]\begin{gathered} U_h=(5\times10^{-3})\times(9.8\text{ m/s}^2)\times(12\text{ m}) \\ =0.588\text{ J} \end{gathered}[/tex]Therefore, the gravitational potential energy when the bullet is 12 m high is 0.588 J.
Part (E).
The velocity of the bullet when it reaches the height of 12 m is given as,
[tex]v^2=u^2-2gh[/tex]Here, v is the velocity when the bullet is 12 m high.
Substituting all known values,
[tex]\begin{gathered} v^2=(85\text{ m/s})^2-2\times(9.8\text{ m/s})\times(12\text{ m}) \\ =6989.8\text{ m}^2\text{ /s}^2 \end{gathered}[/tex]The total mechanical energy when the bullet is 12 m high is,
[tex]ME=U_h+\frac{1}{2}mv^2[/tex]Substituting all known values,
[tex]\begin{gathered} ME=(0.588\text{ J})+\frac{1}{2}\times(5\times10^{-3}\text{ kg})\times(6989.8\text{ m}^2\text{ /s}^2) \\ =18.0625\text{ J} \end{gathered}[/tex]Therefore, the total mechanical energy ME when the bullet is 12 m high is 18.0625 J.
Part (F),
The velocity when the bullet is 12 m high is given as,
[tex]v=\sqrt[]{u^2-2gh}[/tex]Substituting all known values,
[tex]\begin{gathered} v=\sqrt[]{(85\text{ m/s})^2-2\times(9.8\text{ m/s}^2)\times(12\text{ m})} \\ \approx83.605\text{ m/s} \end{gathered}[/tex]Therefore, the velocity when the bullet is 12 m high is 83.605 m/s.
Part 3/3 find the thermal energy transferred. Answer in units of KJ
Answers
0.0We are asked to determine the volume of a gas given the moles, the temperature, and the pressure. To do that, we use the following formula:
[tex]PV=nRT[/tex]Where:
[tex]\begin{gathered} P=pressure \\ V=\text{ volume} \\ n=\text{ number of moles} \\ R=\text{ universal gas constant} \\ T=\text{ temperature} \end{gathered}[/tex]Now, we substitute the values for the final state. Since the process is isothermally this means that the final temperature is the same as the initial temperature. we get:
[tex](1.8atm)V_f=(2mol)(8.31415\frac{J}{Kmol})(243K)[/tex]We need to convert the pressure from atmospheres to Pascals. To do that we use the following conversion factor:
[tex]1atm=101325Pa[/tex]Multiplying by the conversion factor we get:
[tex]1.8atm\times\frac{101325Pa}{1atm}=182385Pa[/tex]Now, we substitute the value in the formula:
[tex](182385Pa)V_f=(2mol)(8.3145\times\frac{J}{Kmol})(243K)[/tex]Solving the operations:
[tex](182385Pa)V_f=4040.847J[/tex]Now, we divide both sides by 182385Pa:
[tex]V_f=\frac{4040.847J}{182385Pa}[/tex]Solving the operations:
[tex]V_f=0.022m^3[/tex]Therefore, the final volume is 0.022 cubic meters.
Part B. We are asked to determine the work done. To do that we will use the formula for isothermic work:
[tex]W=nRT\ln(\frac{P_0}{P_f})[/tex]Where:
[tex]P_0,P_f=\text{ initial and final pressure}[/tex]Now, we plug in the values:
[tex]W=(2mol)(8.31451\frac{J}{Kmol})(243K)\ln(\frac{0.21atm}{1.8atm})[/tex]Now, we solve the operations:
[tex]W=-8681.51J[/tex]Therefore, the work done is -8681.51 Joule. To convert to kilojoules we divide by 1000:
[tex]W=-8681.51J\times\frac{1kJ}{1000J}=-8.68kJ[/tex]Part 3. In an isothermic process the change in internal energy is zero, therefore, according to the first law of thermodynamics we have:
[tex]Q-W=0[/tex]Therefore:
[tex]Q=W[/tex]Therefore, the amount of heat is equal to the amount of work. Therefore, the thermal energy transferred is:
[tex]Q=-8.68kJ[/tex]Coulomb's Law equation is: FE = kq1q2/r2In this expression, FE is the electric force between charges q1 and q2 separated by distance r.When the signs of the charges are included for q1 and q2 , the evaluation of Coulomb's Law equation can yield a positive or negative answer for FE .What is the appropriate interpretation of the sign of the numeric evaluation of FE ?(A) If FE is negative, the charges are attracting.(B) If FE is positive, the charges are attracting.
Answers
We know like charges repel amd unlike charges attract.
Thus if one charge is positive and other is negative then both charges will attract each other.
So if the force is negative , the charges are attracting.
Thus the answer is:
(A) If FE is negative, the charges are attracting.
Describe what values you could solve for if you were given kinetic energy?
Answers
The kinetic energy is given by:
[tex]K=\frac{1}{2}mv^2[/tex]From the above equation,
we can solve from the mass m if velocity is given
or for the velocity if mass m is given
Two positive charge spheres, the spheres are separated by 0.40 m. The charge on the first sphere is 100 microcoulombs and the
charge on the second sphere has 30 microcoulombs. Calculate the Electric Force on the charges?
Answers
Answer: 168.75 N
Explanation:
first, let's convert microcoulombs to coulombs
q1 = 1e-4 C
q2 = 3e-5 C
r = 0.4 m
then use the equation Fe = [tex]\frac{kq_{1} q_{2}}{r^{2} }[/tex]
plug in values --> F = (9e9*1e-4*3e-5)/(0.4)^2
F = 168.75 N
A 0.86 m tall object is placed 3.35 m away from a lens. If the image is 4.58 m tall, how far away from the lens was the image produced? O
Answers
The magnification is the ratio of the image size to the object size. If the image and object are in the same medium, it is just the image distance divided by the object distance:
[tex]M=\frac{i}{o}[/tex]On the other hand:
[tex]M=\frac{h^{\prime}}{h}[/tex]Where h' is the size of the image and h is the size of the object.
Therefore:
[tex]\frac{h^{\prime}}{h}=\frac{i}{o}[/tex]Substitute h'=4.58m, h=0.86m and o=3.35m to find i, the distance from the lens at which the image is produced:
[tex]\begin{gathered} \Rightarrow i=\frac{h^{\prime}}{h}\cdot o \\ =\frac{4.58m}{0.86m}\cdot3.35m \\ =17.84m \end{gathered}[/tex]Therefore, the image is produced 17.84m away from the lens.
An object weighing 88 N is pushed by a 100 N force. What is the acceleration of the object?
Answers
Given data:
* The weight of the object is 88 N.
* The force acting on the object is 100 N.
Solution:
The weight of the object in terms of the mass of the object is,
[tex]W=mg[/tex]where m is the mass of the object, and g is the acceleration due to gravity,
Substituting the known values,
[tex]\begin{gathered} 88=m\times9.8 \\ m=\frac{88}{9.8} \\ m=8.98\text{ kg} \end{gathered}[/tex]According to Newton's second law, the acceleration of the object in terms of the force acting on the object is,
[tex]F=ma[/tex]where a is the acceleration of the object,
Substituting the known values,
[tex]\begin{gathered} 100=8.98\times a \\ a=\frac{100}{8.98} \\ a=11.14ms^{-2} \end{gathered}[/tex]Thus, the acceleration of the object is 11.14 meters per second squared.
6 identical books are lying on a desktop. a tidy student decides to stack the books one on top of the other. if students do 11 J of work width of the spine of each book is 2.5 what is the mass
Answers
An ocean wave usually occurs at a frequency of 2.0 hz what is the period of each wave?
Answers
The period of a wave can be calculated with the formula below:
[tex]T=\frac{1}{f}[/tex]Where f is the frequency.
If the frequency is 2 Hz, the period is:
[tex]T=\frac{1}{2}=0.5\text{ s}[/tex]Therefore the period is 0.5 seconds.
After traveling for 6.0 seconds, a runner reaches a speed of 12 m/s after startingfrom rest. What is the runner's acceleration?
Answers
Given data:
Initial speed of the runner as he starts from the rest;
[tex]u=0[/tex]Final speed of the runner;
[tex]v=12\text{ m/s}[/tex]Time taken;
[tex]t=6.0\text{ s}[/tex]The acceleration of the runner is given as,
[tex]a=\frac{v-u}{t}[/tex]Substituting all known values,
[tex]\begin{gathered} a=\frac{(12\text{ m/s})-0}{(6.0\text{ s})} \\ =2\text{ m/s}^2 \end{gathered}[/tex]Therefore, the acceleration of the runner is 2 m/s².
REMOTE GR 8 SCIENCE / SECTION1 / 9 OF 50Which transformation must occur when a dam uses water to generate energy?O A. Mechanical energy to potential energyоB. Chemical energy to potential energyC. Mechanical energy to electrical energyOD. Chemical energy to electrical energy
Answers
As water flows through the dam, its kinetic energy is used to turn a turbine, a generator convert's the turbine mechanical energy into electrical energy.
C. Mechanical energy to electrical energy
A hiker walks 16.19 m at 18.99 degrees. What is the Y component of hisdisplacement?
Answers
Given:
Distance = 16.9 m
θ = 18.99 degrees.
Let's find the Y component of his displacement.
To find the y-component of his displacement, apply the formula:
[tex]F_y=d\sin \theta[/tex]Hence, to find the y-component of his displacement, substitute values into the formula.
Thus, we have:
[tex]F_y=16.19\sin 18.99[/tex]Solving further:
[tex]F_y=5.27\text{ m}[/tex]Therefore, the Y component of his displacement is 5.27 m
ANSWER:
5.27 m
Two large parallel plates are 17 cm apart and have equal but opposite charges on the surfaces facing each other. An electron is placed half way between the plates. Find the potential difference between the plates if the force on the electron is 5.2×10^(−15) N .
Answers
The potential difference between the plates is equal to 5525 V if the force on the electron is 5.2 ×10⁻¹⁵N.
What is the formula for the electric field of a capacitor?The magnitude of the electric field of the parallel plate capacitor can be calculated from the formula given below:
E = F /q
Where E is the electric field, q is the charge on the electrons and F is the force.
Given the distance between plates, d = 17 cm = 0.17 m
The force, F = 5.2 ×10⁻¹⁵ N, q = 1.6 × 10⁻¹⁹ C
E = 5.2 ×10⁻¹⁵/1.6 × 10⁻¹⁹
E = 32500 N/C
The potential difference , V = E × d
V = 32500 × 0.17
V = 5525 V
Learn more about electric field, here:
https://brainly.com/question/26409781
#SPJ1
Unpolarized light with intensity 455.16 W/m2 passes first through a polarizing filter with its axis vertical, then through a polarizing filter with its axis 33.33o from vertical. What light intensity emerges from the second filter ?
Answers
Given:
The intensity of unpolarized incident light is
[tex]I_0=455.16\text{ W/m}^2[/tex]It passes first through a polarizing filter with its axis vertical
The second polarising filter is at an angle of,
[tex]\theta=33.33\degree[/tex]from the vertical
To find:
What light intensity emerges from the second filter ?
Explanation:
According to the Malus law, the emergent light intensity is,
[tex]\begin{gathered} I=I_0cos^2\theta \\ =455.16\times cos^233.33\degree \\ =317.74\text{ W/m}^2 \end{gathered}[/tex]Hence, the required intensity is
[tex]317.74\text{ W/m}^2[/tex]In the summer time fruit flies are the worst. One morning I woke up to 5 fruit flies in my kitchen. Three hours later there were 13 fruit flies. If the growth rate is continuous, at what rate are the flies increasing? Round answers to four decimal places.
Answers
We are asked to determine the continuous growth rate. To do that we will use the following function:
[tex]P(t)=P_0e^{kt}[/tex]Where "P0" is the initial population, "k" is the growth rate, and "t" is time. Replacing the initial population of 5 we get:
[tex]P(t)=5e^{kt}[/tex]Now we are told that the population is 13 when the time is 3 hours. Replacing we get:
[tex]13=5e^{3k}[/tex]Now we solve for "k". First, by dividing both sides by 5:
[tex]\frac{13}{5}=e^{3k}[/tex]Now we take natural logarithm to both sides:
[tex]\ln (\frac{13}{5})=\ln (e^{3k})[/tex]Now we use the following property of logarithms:
[tex]\ln x^y=y\ln x[/tex]Applying the property:
[tex]\ln (\frac{13}{5})=3k\ln e[/tex]We have that the value of ln(e) is 1, therefore:
[tex]\ln (\frac{13}{5})=3k[/tex]Now we divide both sides by 3:
[tex]\frac{1}{3}\ln (\frac{13}{5})=k[/tex]Solving the operation we get:
[tex]0.319=k[/tex]Therefore, the growth rate is 0.319.
In a dart gun, a spring with k = 400.0 N/m is compressed 8.0 cm when the dart (mass m = 20.0 g) is loaded.
(a) What is the muzzle speed of the dart when the spring is released? Ignore friction.
(b) If the dart gun is located on a table top 2.2 m above the ground, and once the spring is released, it remains compressed by 4 cm, what is the final speed of the dart as it hits the ground?
Answers
The muzzle speed of the dart when the spring is released is 11.3 m/s
The given parameters are
k = spring constant = 400 N/m
m = mass = 20 g = 0.02 kg
Compression = x = 8 cm = 0.08 m
According to the question,
When the dart is loaded, the potential energy is converted into kinetic energy.
Potential Energy (P.E.)
[tex]P.E. =\frac{1}{2} kx^{2}[/tex]
Putting the values,
[tex]P.E. =\frac{1}{2} *400*(0.08)^{2} = 1.28[/tex]
Now, Kinetic Energy (K.E.)
K. E. = [tex]\frac{1}{2} mv^{2}[/tex] = [tex]\frac{1}{2} *0.02*v^{2}= 0.01 v^{2}[/tex]
Now, P.E. = K.E.
[tex]0.01 v^{2} = 1.28 \\\\v^{2} =\frac{1.28}{0.01} \\\\v^{2} = 128\\ \\v = 11.3[/tex]
Hence, the muzzle speed of the dart when the spring is released is 11.3 m/s
To read more about speed, visit https://brainly.com/question/28224010
#SPJ1
it is known that the mass of the earth is 81 times the mass of the moon. show that the point of weightlessness between the earth and the moon for a spacecraft house occurs at √9/10 of the distance to the moon