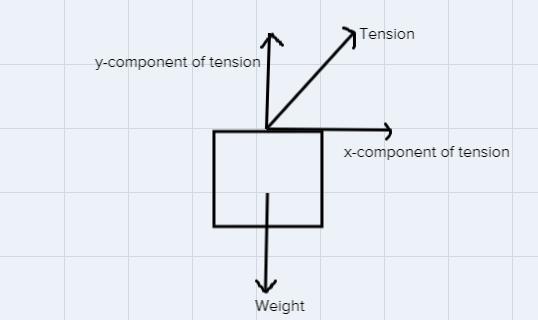
A helicopter flies at a constant altitude towing an airborne 65 kg crate as shown in the diagram. The helicopter and the crate only move in the horizontal direction and have an acceleration of 3.0 m/s21) find the vertical component of the tension in the cable (in Newtons). Ignore the effects of air resistance.2) find the magnitude of the tension in the cable (in Newtons). Ignore the effects of air resistance.3) find the angle(with respect to the horizontal) of the tension in the cable (in degrees). Ignore the effects of air resistance.

Answers
Given data:
* The weight of the crate is 65 kg.
* The acceleration of crate and helicopter is,
[tex]a=3ms^{-2}[/tex]Solution:
(1). The forces acting on the crate is represented as,
The y-component of tension is balancing the weight of the crate.
Thus, the y-component (vertical) of tension is,
[tex]\begin{gathered} T_y=W \\ T_y=mg \end{gathered}[/tex]Where m is the mass of crate and g is the acceleration due to gravity,
Substituting the known values,
[tex]\begin{gathered} T_y=65\times9.8 \\ T_y=637\text{ N} \end{gathered}[/tex]Thus, the vertical component of the tesnion is 637 N.
(2). The x-component of tension in the cable is,
[tex]\begin{gathered} T_x=ma \\ T_x=65\times3 \\ T_x=195\text{ N} \end{gathered}[/tex]Thus, the tension in the cable is,
[tex]\begin{gathered} T=\sqrt[]{T^2_x+T^2_y} \\ T=\sqrt[]{195^2^{}+637^2} \\ T=666.2\text{ N} \end{gathered}[/tex]Hence, the tesnion in the cable is 666.2 N.
(3). The angle of tension with the horizontal is,
[tex]\begin{gathered} \tan (\theta)=\frac{T_y}{T_x} \\ \tan (\theta)=\frac{637}{195} \\ \tan (\theta)=3.3 \\ \theta=73.14^{\circ} \end{gathered}[/tex]Thus, the angle made by the tension with the horizontal is 73.14 degree.
Related Questions
What 2 factors affect the Kinetic Energy of an object? Which of the 2 factors has more of an influence? Explain. What are the 2 units?
Answers
Kinetic energy is a form of energy that an object or a particle has by reason of its motion.
[tex]K=\frac{1}{2}mv^2[/tex]m: mass
v: velocity
velocity has more influence
m: kg
v: m/s
Jenna manipulated the equation 4x+7=10 by adding -7 to both sides. Which of the following properties justifies this manipulation?1. The associative property of addition.2. The addition property of equality.3. The commutative property of addition.4. The multiplication property of equality.
Answers
2. The addition property of equality.
Explanation
Step 1
[tex]\begin{gathered} 4x+7=10 \\ \text{Jenna added -7 ( or subtract 7) to both sides, so} \\ 4x+7-7=10-7 \\ 4x=3 \end{gathered}[/tex]she applied the addition property for inequalities. it states that if an inequality exists, adding or subtracting the same number on both sides does not change the inequality.
so, the answer is
2. The addition property of equality.
An organ pipe that is closed at one end has a length of 3 m. What is the second longest harmonic wavelength for sound waves in this pipe
Answers
Given
Lenght 3m
Procedure
The relationships between the standing wave pattern for a given harmonic and the length-wavelength relationships for closed-end air columns are summarized below.
Harmonic # 3
[tex]\begin{gathered} \lambda=\frac{4}{3}\cdot L \\ \lambda=\frac{4}{3}\cdot3 \\ \lambda=4\text{ m} \end{gathered}[/tex]The second-longest wavelength would be 4m
the heat in Yravels at the of lines. This is also radiation known as and/or write one phrase below each of these terms e heat conduction
Answers
Using the concept of Heat radiation, we have described conduction, convection, and radiation,
Heat can travel from one place to another in several ways. The different modes of the heat transfer include: Conduction, Convection, Radiation
Meanwhile, if the temperature difference exists between the two systems, heat will find a way to transfer from higher to the lower system.
Conduction is defined as:
The process of transmission of energy from one particle of the medium to another with the particles being in direct contact with a each other.
Following are the examples of the conduction:
Ironing of clothes is a example of conduction where the heat is conducted from the iron to the clothes.
Heat is transferred from hands to ice cube resulting in a melting of an ice cube when held in hands.
Convection is defined as the:
The movement of fluid molecules from higher temperature regions to lower temperature regions.
Examples of the convection include:
Boiling of water, that is molecules that are denser move at bottom while the molecules which are less dense move upwards resulting in a circular motion of the molecules so that water gets heated.
Warm water around a equator moves towards the poles while cooler water at the poles moves towards the equator.
Radiation is defined as:
Radiant heat is present in some or other form in our daily lives. Thermal radiations are referred to as the radiant heat. Thermal radiation is generated by the emission of the electromagnetic waves.
Following are the examples of the radiation:
Microwave radiation emitted in the oven is an example of radiation.
UV rays coming from the sun is a example of radiation.
To know more about Heat radiation, visit here:
https://brainly.com/question/13163856
#SPJ9
what is the wavelength of 2.6 million Hz ultrasound as it travels through human tissue ?
Answers
The wavelength of ultrasound waves can be given as,
[tex]\lambda=\frac{v}{f}[/tex]The speed of waves in human tissue is 1540 m/s.
Plug in the known values,
[tex]\begin{gathered} \lambda=\frac{1540\text{ m/s}}{(2.6\text{ million Hz)(}\frac{10^6}{1\text{ million}})}(\frac{10^3\text{ mm}}{1\text{ m}}) \\ =0.592\text{ mm} \end{gathered}[/tex]Thus, the wavelength of waves in human tissue is 0.592 m.
6. A van of mass 1200 kg was moving at a velocity of 8 m/s when it was involved in a head-on collisionwith a lorry moving in the opposite direction. Assuming that the van came to a stop after the collision...(a) calculate the momentum of the van before the collision;(b) calculate the momentum of the van after the collision(c) find the change in momentum of the van (d) if the van took .30 s to stop, calculate the force that acted on each driver
Answers
Given data:
* The mass of the van is 1200 kg.
* The velocity of the van before the collision is 8 m/s.
* The velocity of the van after the collision is 0 m/s.
Solution:
(a). The momentum of the van before the collision is,
[tex]p_i=mv_i[/tex]where m is the mass of van, p_i is the momentum of van before the collision, and v_i is the velocity of van before the collision,
[tex]\begin{gathered} p_i=1200\times8 \\ p_i=9600kgms^{-1^{}} \end{gathered}[/tex]Thus, the momentum of the van before the collision is 9600 kgm/s.
(b). The momentum of the van after the collision is,
[tex]p_f=mv_f[/tex]weere p_f is the final momentum, and v_f is the final velocity of the van,
Substituting the known values,
[tex]\begin{gathered} p_f=1200\times0 \\ p_f=0^{} \end{gathered}[/tex]Thus, the momentum of the van after the collision is 0 kgm/s.
(c). The change in the momentum of the van is,
[tex]\begin{gathered} dp=p_f-p_i \\ dp=0-9600 \\ dp=-9600kgms^{-1} \end{gathered}[/tex]Here, the negative sign indicates that the momentum of van is decreasing with time.
Thus, the change in the momentum of the van is -9600 kgm/s.
(d). According to the Newton's second law, the force acting on the van in terms of the change in momentum is,
[tex]F=\frac{dp}{dt}[/tex]where dt is the time interval in which the momentum of the van changes,
Substituting the known values,
[tex]\begin{gathered} F=-\frac{9600}{0.30} \\ F=-32000\text{ N} \\ F=-32\times10^3\text{ N} \\ F=-32\text{ kN} \end{gathered}[/tex]Here, the negative sign is indicating the direction of force acting on the van is opposite to the direction of motion of van before the collision.
Thus, the force acting on the van is -32 kN.
Please help me I know it’s not the second choice
Answers
The wavelength of a light wave as it passes through a material is 657.61 nm with a speed of 232,536,355.7 m/s. What is the frequency of this wave?
Answers
Given:
The wavelength of light is
[tex]\begin{gathered} \lambda\text{ = 657.61 nm} \\ =657.61\times10^{-9}\text{ m} \end{gathered}[/tex]The speed is v = 232536355.7 m/s
Required: The frequency of the wave.
Explanation:
The frequency can be calculated by the formula
[tex]f=\frac{v}{\lambda}[/tex]On substituting the values, the frequency will be
[tex]\begin{gathered} f=\text{ }\frac{232536355.7}{657.61\times10^{-9}} \\ =3.536\times10^{14}\text{ s} \end{gathered}[/tex]Final Answer: The frequency of the wave is 3.536e14 s
A student pushes a heavy box that is originally stationary across the floor with a force 112 N. What is the coefficient of static friction between the classroom floor and the 140 N box?
Answers
Given data:
* The force applied on the heavy box is,
[tex]F_a=112\text{ N}[/tex]* The weight of the heavy box is,
[tex]w=140\text{ N}[/tex]Solution:
The frictional force acting on the box is,
[tex]\begin{gathered} F_r=\mu\times w \\ \mu\text{ is the coefficient of friction,} \end{gathered}[/tex]The frictional force acting on the heavy box is equal to the applied force as the heavy box is not moving under the action of applied force.
Thus,
[tex]\begin{gathered} F_r=F_a \\ \mu\times w=112 \\ \mu\times140=112 \\ \mu=\frac{112}{140} \end{gathered}[/tex]By simplifying,
[tex]\mu=0.8\text{ }[/tex]Thus, the coefficient of friction between the floor and the box is 0.8.
Joanne drives her car with a mass of 1000 kg at a speed of 16m/s. what is the
the magnitude of road friction force needed to bring her car to a halt in 14s .
Answers
The frictional force will be the product of mass and the deceleration of the car which is 1142.9 N
What is Friction ?Friction is a force that opposes motion. It depends on the surface in contact and independent on the area of the surface.
Given that Joanne drives her car with a mass of 1000 kg at a speed of 16m/s. Before we calculate the the magnitude of road friction force needed to bring her car to a halt in 14s, let us first list out all the necessary parameters
Mass m = 1000 kgInitial velocity u = 16 m/sFinal velocity v = 0 m/sTime t = 14 sAcceleration a = ?Frictional Force F = ?The Frictional Force F = ma
From first equation of motion, v = u - at
Substitute the necessary parameters into the equation
0 = 16 - (a × 14)
14a = 16
a = 16/14
a = 1.143 m/s²
Then Frictional Force F = 1000 × 1.143
F = 1142.9 N
Therefore, the magnitude of road frictional force needed to bring her car to a halt in 14s is 1142.9 N
Learn more about Friction here: https://brainly.com/question/24386803
#SPJ1
A train is traveling at 100 mil/hr and travels for 10 hrs . How far did it travel ?
Answers
Givens.
• The speed is 100 mi/hr.
,• The time elapsed is 10 hr.
To find the distance traveled, use the constant motion formula.
[tex]d=vt[/tex]Where, v = 100 mi/hr and t = 10 hr.
[tex]\begin{gathered} d=100\cdot\frac{mi}{hr}\cdot10hr \\ d=1000mi \end{gathered}[/tex]Therefore, the train traveled 1000 miles.
An astronaut, of mass 95.0 kg, sits on a newton scale as the shuttle takes off. The newton scale reads 5500 N. What is the acceleration of the shuttle?
Answers
Given data:
* The mass of the astronaut is m = 95 kg.
* The force read by the Newton scale when the shuttle takes off is F = 5500 N.
Solution:
According to Newton's second law, the force on the astronaut in terms of the acceleration and mass is,
[tex]\begin{gathered} F=\text{ma} \\ a=\frac{F}{m} \end{gathered}[/tex]Substituting the known values,
[tex]\begin{gathered} a=\frac{5500}{95} \\ a=57.9ms^{-2} \\ a\approx58ms^{-2} \end{gathered}[/tex]The shuttle and the astronaut are moving with the same acceleration.
Thus, the acceleration of the shuttle is 58 meters per second squared.
Which of the following descriptions best describes all of the factors that need to be considered when
determining an object's terminal velocity? (1 point)
O air density and the object's drag coefficient
O the object's weight and area it presents
O the object's weight and area it presents, as well as air density
O the object's weight, length, and width
Answers
All of the factors that need to be considered when determining an object's terminal velocity are the object's weight and area it presents, as well as air density.
option C is the correct answer
What is terminal velocity?Terminal velocity is obtained when the speed of a moving object is no longer increasing or decreasing. That is the object's acceleration (or deceleration) is zero.
Mathematically, the formula for terminal velocity is given as;
V = √(2mg)/(ρAC)
where;
m is the mass of the falling objectg is the acceleration due to gravityρ is the density of the fluid through which the object is fallingA is the projected area of the objectC is the drag coefficientThus, the variables to consider in determining terminal velocity of an object incudes the area, density of air, mass, etc.
Learn more about terminal velocity here: https://brainly.com/question/25905661
#SPJ1
A 5000. kg elevator accelerates at 3.0m/s? as it begins to move upward. Calculate the tension in the cable
Answers
Given data;
* The mass of the elevator is 5000 kg.
* The acceleration of the elevator is,
[tex]a=3ms^{-2}[/tex]Solution:
The free body diagram of the elevator is,
The weight of the elevator is,
[tex]W=mg[/tex]where m is the mass of the elevator and g is the acceleration due to gravity,
Substituting the known values,
[tex]\begin{gathered} W=5000\times9.8 \\ W=49000\text{ N} \end{gathered}[/tex]The net force acting on the elevator is,
[tex]F_{\text{net}}=ma[/tex]where a is the acceleration of the elevator moving upwards,
Substituting the known values,
[tex]\begin{gathered} F_{\text{net}}=5000\times3 \\ F_{\text{net}}=15000\text{ N} \end{gathered}[/tex]From the free body diagram, the tension acting on the cable is,
[tex]\begin{gathered} T-W=F_{\text{net}} \\ T=F_{\text{net}}+W \end{gathered}[/tex]Substituting the known values,
[tex]\begin{gathered} T=15000+49000 \\ T=64000\text{ N} \\ T=64\text{ kN} \end{gathered}[/tex]Thus, the tension acting in the cable is 64 kN.
A truck covers 40.0 m in 9.45 s while uniformly slowing down to a final velocity of 2.10 m/s.(a) Find the truck's original speed._____ m/s(b) Find its acceleration._____ m/s2
Answers
(a)
In order to find the original speed, let's use the formula below to find an expression for the acceleration:
[tex]\begin{gathered} V=V_0+a\cdot t\\ \\ 2.1=V_0+a\cdot9.45\\ \\ a=\frac{2.1-V_0}{9.45} \end{gathered}[/tex]Now, we can use the following formula to find the initial speed:
[tex]\begin{gathered} \Delta S=V_0t+\frac{at^2}{2}\\ \\ 40=V_0\cdot9.45+\frac{\frac{(2.1-V_0)}{9.45}\cdot9.45^2}{2}\\ \\ 40=9.45V_0+4.725(2.1-V_0)\\ \\ 40=9.45V_0+9.9225-4.725V_0\\ \\ 4.725V_0=40-9.9225\\ \\ V_0=\frac{30.0775}{4.725}\\ \\ V_0=6.3656\text{ m/s} \end{gathered}[/tex](b)
Now, calculating the acceleration, we have:
[tex]\begin{gathered} a=\frac{2.1-6.3656}{9.45}\\ \\ a=-0.4514\text{ m/s^^b2} \end{gathered}[/tex]If you ride a bicycle 36 m in 12 seconds, what is your speed?O A. 0.3 m/sB. 2 m/sC. 3 m/sD. 0.09 m/s
Answers
We are given that the distance is 36 m and the time is 12 seconds.
We are asked to find the speed.
Recall that the time, speed, and distance formula is given by
[tex]v=\frac{x}{t}[/tex]Where v is the speed, x is the distance, and t is the time.
Let us substitute the given values into the above formula.
[tex]\begin{gathered} v=\frac{36}{12} \\ v=3\; \; \frac{m}{s} \end{gathered}[/tex]Therefore, the speed is 3 m/s
Option C is the correct answer.
How much heat is needed to bring 25.5 g of water from 29.3 °C to 43.87 °C.Q =m=ΔT= C=solution =
Answers
We are given the following information
Mass of water = 25.5 g
Initial temperature of water = 29.3 °C
Final temperature of water = 43.87 °C
The specific heat capacity of water is 4.186 J/g.°C
The amount of heat required is given by
[tex]\begin{gathered} Q=m\cdot c\cdot\Delta T \\ Q=m\cdot c\cdot(T_f-T_i) \end{gathered}[/tex]Let us substitute the given values into the above formula
[tex]\begin{gathered} Q=25.5\times4.186\cdot(43.87-29.3) \\ Q=1,555.25\; J \end{gathered}[/tex]Therefore, we need 1,555.25 Joules of heat to bring 25.5 g of water from 29.3 °C to 43.87 °C.
A girl throws a ball vertically downward at 10m/s from the roof of a building 20m high. Whatwill its speed be when it strikes the ground?
Answers
Answer:
22.18 m/s
Explanation:
We will use the following equation:
[tex]v^2_f_{}=v^2_i+2ay[/tex]Where vf is the final velocity
vi is the initial velocity, so it is -10 m/s
a is gravity, so it is -9.8 m/s²
y is the change in the height so it is -20 m
Therefore, replacing the values, we get:
[tex]\begin{gathered} v^2_f=(-10)^2+2(-9.8)(-20) \\ v^2_f=100+392 \\ v^2_f=492 \\ v_f=\sqrt[]{492}=22.18\text{ m/s} \end{gathered}[/tex]So, the ball strikes the ground at 22.18 m/s
Please help me create a table and graph for the experiment below.Mass of bob: 25g, Time noted: 0.54 s, 0.54 s, 0.54 sMass of bob: 50g, Time noted: 0.54 s, 0.56 s, 0.49 sMass of bob: 100g: Time noted: 0.53 s, 0.53 s, 0.46 s
Answers
Given:
Mass of bob: 25g, Time noted: 0.54 s, 0.54 s, 0.54 s
Mass of bob: 50g, Time noted: 0.54 s, 0.56 s, 0.49 s
Mass of bob: 100g: Time noted: 0.53 s, 0.53 s, 0.46 s
To find:
The average time period for each mass of the pendulum bob.
Explanation:
As the sensor records the time it takes for the pendulum to complete one-half of the period, the time period of the pendulum can be calculated by multiplying the recorded value by 2.
For the bob of mass 25 g,
Period (s) Trial 1: 0.54 s × 2 = 1.08 s
Period (s) Trial 2: 0.54 s × 2 = 1.08 s
Period (s) Trial 3: 0.54 s × 2 = 1.08 s
Average Period (s): T = (1.08 s + 1.08 s + 1.08 s)/3 = 1.08 s
For the bob of mass 50 g,
Period (s) Trial 1: 0.54 s × 2 = 1.08 s
Period (s) Trial 2: 0.56 s × 2 = 1.12 s
Period (s) Trial 3: 0.49 s × 2 = 0.98 s
Average Period (s): T = (1.08 s + 1.12 s + 0.98 s)/3 = 1.06 s
For the bob of mass 100 g,
Period (s) Trial 1: 0.53 s × 2 = 1.06 s
Period (s) Trial 2: 0.53 s × 2 = 1.06 s
Period (s) Trial 3: 0.46 s × 2 = 0.92 s
Average Period (s): T = (1.06 s + 1.06 s + 0.92 s)/3 = 1.013 s
Final answer:
The average value of the period is
For bob of mass 25 g, Average Period = 1.08 s
For bob of mass 50 g, Average Period = 1.06 s
For bob of mass 100 g, Average Period = 1.013 s
Alexander's hobby is dirt biking. On one occasion last weekend, he accelerated from rest to 12.8 m/s in 4.43 seconds. He then maintained this speed for 8.83 seconds. Seeing a coyote run cross the trail ahead of him, he abruptly stops in 6.36 seconds. Determine Alexander's average speed for this motion?
Answers
The average speed of Alexander, given that he accelerated from rest to 12.8 m/s in 4.43 seconds is 12.8 m/s
How do I determine the average speed of Alexander?First, we shall determine the distance travelled in 4.43 seconds. This is shown below:
Speed = 12.8 m/sTime = 4.43 secondDistance =?Distance = speed × time
Distance = 12.8 × 4.43
Distance = 56.704 m
Next, we shall determine the distance travelled in 8.83 seconds. This is shown below:
Speed = 12.8 m/sTime = 8.83 secondDistance =?Distance = speed × time
Distance = 12.8 × 8.83
Distance = 113.024 m
Next, we shall determine the distance travelled in 6.36 seconds. This is shown below:
Speed = 12.8 m/sTime = 6.36 secondDistance =?Distance = speed × time
Distance = 12.8 × 6.36
Distance = 81.408 m
Finally, we shall determine the average speed of Alexander. This is shown below:
Total distance = 56.704 + 113.024 + 81.408 = 251.136 mTotal time = 4.43 + 8.83 + 6.36 = 19.62Average speed =?Average speed = Total distance / total time
Average speed = 251.136 / 19.62
Average speed = 12.8 m/s
Thus, the average speed is 12.8 m/s
Learn more about average speed:
https://brainly.com/question/12025128
#SPJ1
Question: imagine the decay of a very unusual particle that has a charge of Q = +24e. If it decays into 12 particles, 3 of which have electrical charges of +2e each, what is the collective charge of the other 9 particles?
Answers
According to the law of charge conservation,
The net charge of the system before and after the decay should remain constant.
As the charge before the decay is +24e.
Thus, the net charge after the decay should be +24e.
Given that, the charge on 3 particles out of 12 is +2e each.
Thus, collective charge of the other 9 particles is,
[tex]\begin{gathered} q=Q-3(+2e) \\ q=24e-6e \\ q=+18e \end{gathered}[/tex]Thus, the collective charge on the other 9 particles is +18e.
Why doesn't an object falling from an airplane continue to accelerate? (1 point)
O Gravity's force diminishes as the object nears the ground.
O Air resistance on the object will eventually equal the force of force of gravity.
O The object's weight varies as it nears the ground.
O Hitting the ground stops the object's acceleration.
Answers
A falling object accelerates as it descends. The quantity of air resistance rises in proportion to the speed. The pull of gravity eventually is balanced by the force of air resistance as it grows. The item will cease accelerating since there is no net force at this point in time (0 Newton).
Since the upward force of air resistance eventually equals the downward force of gravity, a falling item cannot continue to accelerate indefinitely before reaching its terminal velocity.In contrast to air resistance, which operates in the opposite direction and slows acceleration, gravity causes objects to accelerate downhill. Greater surface area falling objects encounter more air resistance. In the absence of air, or in a vacuum, all objects fall with the same precise rate of acceleration.To know more about gravity
https://brainly.com/question/28651985
#SPJ1
Answer: (B). Air resistance on the object will eventually equal the force of force of gravity.
Explanation:
hello can you help me with my AP physics assignment
Answers
1)
R is the required distance from the starting point. The right triangle representing this scenario is shown below
We would apply pythagorean theorem which is expressed as
hypotenuse^2 = one leg^2 + other leg^2
hypotenuse = R
one leg = 25
other leg = 18
Thus,
R^2 = 25^2 + 18^2 = 949
R = √949
R = 30.81
You're 30.81m from your starting point
2) We would find θ by applying the tangent trigonometric ratio which is expressed as
tanθ = opposite side/adjacent side
opposite side = 25
adjacent side = 18
tanθ = 25/18
θ = tan^-1(25/18)
θ = 54.25 degrees
Position = 54.25 degrees west of north
Please help me solve From a previous question, the index of refraction of the liquid is 1.37
Answers
ANSWER
EXPLANATION
From the previous part, we have that the index of refraction of the liquid is 1.37, so we have to replace this in the equation and solve,
[tex]\sin\theta_c=\frac{n_{air}}{n_{liquid}}=\frac{1.00}{1.37}\approx0.73[/tex]And then, take the inverse of the sine to find the critical angle,
[tex]\theta_c=\sin^{-1}0.73\approx46.9\degree[/tex]Hence, the critical angle is 46.9°, rounded to the nearest tenth.
A substance has a mass of 15,000 kg and a volume of 30 m 3 . What is the density of thesubstance?
Answers
ANSWER
500 kg/m³
EXPLANATION
Given:
• The mass of the substance, m = 15,000 kg
,• The volume of the substance, V = 30 m³
Find:
• The density of the substance, ρ
The density of a substance of mass m and volume V is,
[tex]\rho=\frac{m}{V}[/tex]Substitute the known values and solve,
[tex]\rho=\frac{15,000kg}{30m^3}=500kg/m^3[/tex]Hence, the density of the substance is 500 kg/m³.
A periodic wave has a frequency of 3.2 Hz. What is the wave period?answer in:____ s
Answers
Given:
Frequency of wave, f = 3.2 Hz.
Let's find the period of the wave.
To find the wave period, apply the formula:
[tex]T=\frac{1}{f}[/tex]Where:
T is the period in seconds
f is the frequency hertz.
Thus, we have:
[tex]\begin{gathered} T=\frac{1}{3.2} \\ \\ T=0.3125\text{ s} \end{gathered}[/tex]Therefore, the wave period is 0.3125 seconds.
ANSWER:
0.3125 s
Jontell finds a giant spring that has a 350N/m spring constant. Jontell figures out how to compress is 1.5m. If Jontell and his spring propelled cart's mass is 85kg, how fast is he going after the push fromthe spring? PEspring1/2*k*x?^2
Answers
Given data
*The given mass of the propelled cart's is m = 85 kg
*The given spring constant is k = 350 N/m
*The spring compresses at a distance is x = 1.5 m
The formula for the speed is given by the conservation of energy as
[tex]\begin{gathered} U_{p.e}=U_k \\ \frac{1}{2}kx^2=\frac{1}{2}mv^2 \\ v=\sqrt[]{\frac{kx^2}{m}} \end{gathered}[/tex]Substitute the known values in the above expression as
[tex]\begin{gathered} v=\sqrt[]{\frac{350\times(1.5)^2}{85}} \\ =3.04\text{ m/s} \end{gathered}[/tex]Given a material of specific heat c in Cal/gramC^o and mass 6 grams. If the material is heated by absorbing 7 calories of heat then which of these expressions yields the change in temperature of the material in Celsius degrees? A)7 divided by (c - 6) B)7 times (c - 6) C)7 divided by (6 times c)
Answers
Given:
The mass is m = 6 grams.
The heat absorbed is Q = 7 calories.
The unit of specific heat, c of the material is cal/gram degree Celsius
To find the change in temperature of the material in degrees Celsius.
Explanation:
The formula to calculate the temperature change is
[tex]\begin{gathered} Q\text{ = mc}\Delta T \\ \Delta T=\frac{Q}{mc} \end{gathered}[/tex]Substituting the values, the change in temperature will be
[tex]\Delta T\text{ = }\frac{7}{6\times c}[/tex]Final Answer: The change in temperature will be 7 divided by (6 times c).
A block has a velocity of 6 m/s to the East and 360 J of kinetic energy. The block is pushed West with a 30 N external force, while the block moves 3 m East. How much work is done by the force?
Answers
Work done will be 270 J
What is work energy theorem?
The work-energy theorem states that the net work done by the forces on an object equals the change in its kinetic energy.
according to work force theorem
Work done = Force x direction = FD Cosθ
Even if the force is applied to the opposite direction, the box will move in the direction of East. Firstly it was already 6m towards East and after applying force, the box moves further 3m towards same direction i.e East.
= 30 N x (9) cos 0⁰
= cos 0⁰ is 1
= 270 J
270 J work is done by the force.
learn more about work energy theorem: brainly.com/question/10063455
#SPJ9
Question 3 of 5Molly wants to measure how hot water is when it begins to boil. What toolshould she use?O A. A graduated cylinderO B. A thermometerO C. CalipersD. A test tube
Answers
To find
Molly wants to measure how hot water is when it begins to boil. What tool should she use?
Explanation
A graduated cylinder is used to measure the volume of liquid.
Thermometer is a device which is used to measure temperature.
Calipers are used to measure dimensions of objects
A test tube is used to hold liquid during laboratory experiments
Conclusion
To measure the hotness of water she needs
B. A thermometer